Chronic Kidney Disease
Condition Basics
What is chronic kidney disease?
Chronic kidney disease means your kidneys have not worked right for a while. It most often happens as a result of damage to your kidneys over many years. But it can also happen quickly.
Your kidneys have an important job. They remove waste and extra fluid from your blood. This waste and fluid goes out of your body in your urine.
When your kidneys don't work as they should, wastes build up in your blood. This makes you sick.
Chronic kidney disease is also called chronic renal failure. Or it may be called chronic renal insufficiency.
What causes it?
Chronic kidney disease is caused by damage to the kidneys. The most common causes of this damage are many years of uncontrolled high blood pressure or high blood sugar from uncontrolled diabetes. Other things can cause it too, including kidney diseases and long-term use of certain medicines.
What are the symptoms?
Many people with chronic kidney disease don't have symptoms. If your kidneys get worse and start to fail, you may have symptoms. For example, you may urinate less than normal, feel very tired or sleepy, have swelling and weight gain, or have trouble sleeping.
How is it diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask you about past kidney problems. You will be asked if you have a family history of kidney disease. Your doctor will also want to know what medicines you take. This includes prescription and over-the-counter medicines.
Your doctor will do blood and urine tests to check how well your kidneys are working. This will help your doctor see how well your kidneys filter your blood.
You may have a test, such as an ultrasound or CT scan. These tests let your doctor look at a picture of your kidneys. This can help your doctor measure the size of your kidneys and see if anything is blocking your urine flow.
In some cases, your doctor may take a tiny sample of kidney tissue. This is called a biopsy. It helps the doctor find out what caused the kidney disease.
How is chronic kidney disease treated?
The first step is to treat the disease that's causing kidney damage. In most cases, this is diabetes or high blood pressure. Managing your blood pressure and blood sugar may slow the damage to your kidneys.
You'll probably need to take medicine. Take it as prescribed.
Lifestyle changes can help slow kidney disease or improve other problems that make kidney disease worse.
- Follow a diet that's easy on your kidneys. You may need to limit salt (sodium) and protein and watch your fluid intake.
- Be active.
- Don't smoke or use tobacco.
- Limit alcohol and avoid illegal drugs.
- Avoid medicines that can harm your kidneys. Let your doctor know all of the prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Talk with your doctor before taking anything new.
If you have kidney failure, your doctor may recommend that you start dialysis. Or it may be better to get a new kidney (transplant).
What is end-stage renal disease?
End-stage renal disease means that your kidneys may no longer be able to keep you alive. When your kidneys get to the point where they can no longer remove waste, you may need dialysis or a new kidney. When you understand your options, you can make the choice that's best for you.
End-stage renal disease affects your whole body. It can cause serious heart, bone, lung, blood, and brain problems.
Health Tools
Health Tools help you make wise health decisions or take action to improve your health.
Advance Care Planning: Should I Stop Kidney Dialysis?Advance Care Planning: Should I Stop Kidney Dialysis? Kidney Failure: Should I Start Dialysis?Kidney Failure: Should I Start Dialysis? Kidney Failure: What Type of Dialysis Should I Have?Kidney Failure: What Type of Dialysis Should I Have? Kidney Failure: When Should I Start Dialysis?Kidney Failure: When Should I Start Dialysis?
Diabetes: Checking Your Blood SugarDiabetes: Checking Your Blood Sugar High Blood Pressure: Checking Your Blood Pressure at HomeHigh Blood Pressure: Checking Your Blood Pressure at Home High Cholesterol: Making Lifestyle ChangesHigh Cholesterol: Making Lifestyle Changes Kidney Disease: Changing Your DietKidney Disease: Changing Your Diet
Cause
Chronic kidney disease is caused by damage to the kidneys. The most common causes of this damage are:
- Diabetes. High blood sugar levels caused by diabetes can damage blood vessels in the kidneys. If blood sugar stays high over many years, this damage slowly reduces kidney function.
- High blood pressure. If it isn't treated, high blood pressure can damage blood vessels, which can lead to damage in the kidneys. Blood pressure often rises with chronic kidney disease.
Other things that can lead to chronic kidney disease include:
- Kidney diseases you were born with, such as polycystic kidney disease.
- Kidney infections.
- A narrowed or blocked renal artery. This artery carries blood to the kidneys.
- Long-term use of medicines that can damage the kidneys, such as ibuprofen and some antibiotics.
Learn more
-
Diabetic Kidney DiseaseDiabetic Kidney Disease -
High Blood PressureHigh Blood Pressure
What Increases Your Risk
The main factors that put you at risk of chronic kidney disease include:
- Having high blood pressure, diabetes, or a family history of either. These conditions can damage the small blood vessels in the kidneys. They are the major causes of chronic kidney disease.
- Being in the obese weight range.
- Taking certain medicines that can damage kidneys over the long term. Examples are pain relievers called NSAIDs and certain antibiotics.
- Being older. The kidneys begin to work less well as people age.
- Being African American or Native American.
- Being male.
Prevention
Chronic kidney disease may sometimes be prevented by controlling the other diseases or factors that can contribute to kidney disease. People who have already developed
- Manage your blood pressure.
Work with your doctor to keep your blood pressure under control. Learn to check your blood pressure at home.
- Manage your blood sugar.
If you have diabetes, keep your blood sugar within a target range. Talk with your doctor about how often to check your blood sugar.
- Stay at a healthy weight.
This can help you prevent other diseases, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease.
- Control your cholesterol levels.
- Don't smoke or use other tobacco products.
Smoking can lead to
atherosclerosisatherosclerosis , which reduces blood flow to the kidneys.
Learn more
-
Diabetes: Checking Your Blood SugarDiabetes: Checking Your Blood Sugar -
High Blood Pressure: Checking Your Blood Pressure at HomeHigh Blood Pressure: Checking Your Blood Pressure at Home -
High Cholesterol: Making Lifestyle ChangesHigh Cholesterol: Making Lifestyle Changes -
Quitting SmokingQuitting Smoking -
Weight ManagementWeight Management
Symptoms
Many people with chronic kidney disease don't have symptoms. If your kidneys get worse and start to fail, you may:
- Have swelling and weight gain. This is from the extra fluid in your tissues. It is called edema (say "ih-DEE-muh").
- Often feel sick to your stomach (nauseated) or vomit.
- Have trouble sleeping.
- Urinate less than normal.
- Have trouble thinking clearly.
- Feel very tired.
What Happens
In the early stages of the disease, your kidneys are still able to regulate the fluids, salts, and waste products in your body. But if you keep losing kidney function, you may start to have problems, or complications.
How long it takes for the kidney disease to get worse depends on your condition. Sometimes it gets worse very slowly over many years. Or it may get worse more quickly.
When kidney function falls below a certain point, it is called kidney failure. Kidney failure affects your whole body. It can cause serious heart, bone, and brain problems and make you feel very ill. Untreated kidney failure can cause death.
Complications of chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease can cause problems throughout your body.
- Anemia. You may feel weak, have pale skin, and feel tired because the kidneys can't produce enough of the hormone needed to make red blood cells.
- Electrolyte imbalance. When the kidneys can't filter out certain chemicals, you may have an irregular heartbeat, muscle weakness, or other problems.
- Uremic syndrome. You may be tired, have nausea and vomiting, not have an appetite, or be unable to sleep when substances build up in your blood. The substances can be poisonous if they reach high levels.
- Heart disease. Chronic kidney disease speeds up hardening of the arteries and increases the risk of stroke, heart attack, heart failure, and death.
- Bone disease. Abnormal levels of substances, such as calcium and phosphate, can lead to this.
- Fluid buildup. As kidney function gets worse, fluids build up in the body. This can lead to heart failure and pulmonary edema.
Learn more
-
Anemia of Chronic Kidney DiseaseAnemia of Chronic Kidney Disease -
End-Stage Renal DiseaseEnd-Stage Renal Disease -
Stages of Chronic Kidney DiseaseStages of Chronic Kidney Disease
When to Call a Doctor
Call 911 or other emergency services if you have chronic kidney disease and you develop:
- A very slow heart rate (less than 50 beats a minute).
- A very rapid heart rate (more than 120 beats a minute).
- Chest pain or severe shortness of breath.
- Severe muscle weakness.
You can
Call your doctor now if you:
- Have symptoms of uremic syndrome, such as increasing fatigue, nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, or being unable to sleep.
- Vomit blood or have blood in your stools.
Call your doctor if you:
- Are feeling more tired or weak.
- Have swelling of the arms or feet.
- Bruise often or easily or have abnormal bleeding, such as nosebleeds.
- Are being treated with dialysis and you:
- Have belly pain while you are being treated with peritoneal dialysis.
- Have
signs of infectionsigns of infection at your catheter or dialysis access site, such as pus draining from the area. - Have any other problem that your dialysis instruction manual or nurse's instructions say you should call about.
If you have uncontrolled weight loss, discuss this with your doctor during your next visit.
Watchful waiting
A wait-and-see approach is not a good idea if you could have chronic kidney disease. See your doctor. If you have been diagnosed with chronic kidney disease, follow your treatment plan. And call your doctor if you notice any new symptoms.
Exams and Tests
To diagnose chronic kidney disease, your doctor will ask questions about any past kidney problems. Your doctor will also ask if you have a family history of kidney disease and what medicines you take, both prescription and over-the-counter drugs. Your doctor will also do a physical exam and ask if you have a history of smoking. You may also be asked if you have been around certain toxins.
The doctor will also do tests. Tests for chronic kidney disease help find out:
- Whether kidney disease happened suddenly (acute) or has been happening over a long time (chronic).
- What is causing the kidney damage.
- Which treatment is best to help slow kidney damage.
- How well treatment is working.
- When to begin dialysis or have a kidney transplant.
Tests of kidney function
As your kidney function gets worse, the amount of substances such as nitrogen and creatinine (say "kree-AT-uh-neen") in your blood increases. Tests to check how well your kidneys are working include:
- Blood creatinine test.
- Measuring the level of creatinine in your blood helps determine the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). The doctor can use the eGFR to regularly check how well the kidneys are working. The eGFR is also used to find the stage of your kidney disease and to guide decisions about treatment.
- Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) test.
-
This measures how much nitrogen from the waste product urea is in your blood. BUN level rises when the kidneys aren't working well enough to remove urea from the blood.
- Fasting blood glucose test.
-
This is done to measure your blood sugar. High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels in the kidneys.
- Chemistry screen.
-
These blood tests measure levels of waste products and electrolytes in your blood that should be removed by your kidneys.
- Blood test for parathyroid hormone (PTH).
-
This checks the level of PTH, which helps control calcium and phosphorus levels.
- Urinalysis and a urine test for microalbumin.
-
These or other urine tests can measure protein in your urine. Normally there is little or no protein in urine.
Other tests
Your doctor may use other tests to monitor kidney function or to find out whether another kidney disease or condition is contributing to reduced kidney function. These include:
- Renal ultrasound.
-
An ultrasound of the kidney helps the doctor estimate how long you may have had chronic kidney disease. It also checks whether urine flow from the kidneys is blocked. An ultrasound also may help find causes of kidney disease, such as obstruction or polycystic kidney disease.
- Duplex Doppler study or angiogram of the kidney.
-
This may be done to check for problems caused by restricted blood flow (renal artery stenosis).
- Kidney biopsy.
-
This may help find out the cause of chronic kidney disease. After a kidney transplant, a doctor may use this test if it's suspected that the organ is being rejected by your body.
Learn more
-
Abdominal UltrasoundAbdominal Ultrasound -
Albumin Urine TestAlbumin Urine Test -
Blood Glucose TestBlood Glucose Test -
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) TestBlood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Test -
Creatinine and Creatinine Clearance TestsCreatinine and Creatinine Clearance Tests -
Doppler UltrasoundDoppler Ultrasound -
Kidney BiopsyKidney Biopsy
Treatment Overview
Manage your health problems
- If you have diabetes, it's important to keep your blood sugar level in your target range with diet, exercise, and medicines. If your blood sugar level is too high for too long, it can damage your kidneys.
- If you have high blood pressure, it's important to control it with diet, exercise, and any medicines your doctor prescribes.
Treat problems caused by kidney disease
- If your doctor put you on a special diet, stay on the diet.
- If you have kidney failure, you'll probably have two treatment choices. Your doctor may recommend that you start kidney dialysis to filter wastes and extra fluid from your blood. Or it may be better to get a new kidney (transplant). Both treatments have risks and benefits. Talk with your doctor to decide which is best for you.
Practice healthy habits
- Be active. Walking is a good choice. Try for at least 30 minutes on most days of the week.
- Follow a diet that is healthy for your kidneys. A dietitian can help make an eating plan with the right amount of salt (sodium), protein, and fluids.
- Don't smoke. Smoking can make chronic kidney disease worse. If you need help quitting, talk to your doctor about stop-smoking programs and medicines.
- Avoid medicines that can harm your kidneys. These medicines include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Examples of these are ibuprofen and celecoxib. Let your doctor know all of the prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. And talk to your doctor before you take anything new.
- Limit your use of alcohol, and avoid illegal drugs.
Get follow-up care
Go to all follow-up visits. Your doctor will use blood and urine tests to regularly check how well your kidneys are working and decide if you need changes in your treatment plan.
Palliative care
Palliative care is a type of care for people who have a serious illness. It's different from care to cure your illness, called curative treatment. Palliative care provides an extra layer of support that can improve your quality of life—not just in your body, but also in your mind and spirit. Sometimes palliative care is combined with curative treatment.
The kind of care you get depends on what you need. Your goals guide your care. You can get both palliative care and care to treat your illness. You don't have to choose one or the other.
Palliative care can help you manage symptoms, pain, or side effects from treatment. It may help you and those close to you better understand your illness, talk more openly about your feelings, or decide what treatment you want or don't want. It can also help you communicate better with your doctors, nurses, family, and friends.
Learn more
-
Care at the End of LifeCare at the End of Life -
Palliative CarePalliative Care -
Writing an Advance DirectiveWriting an Advance Directive
Self-Care
There are many things you can do at home to slow the progression of chronic kidney disease.
- Manage your blood pressure.
Work with your doctor to keep your blood pressure under control. Learn to check your blood pressure at home.
- If you have diabetes, keep your blood sugar within a target range.
- Stay at a healthy weight.
This can also reduce your risk for
coronary artery diseasecoronary artery disease , diabetes, high blood pressure, and stroke. - Follow the eating plan your dietitian created for you.
Your eating plan will balance your need for calories with your need to limit certain foods, such as sodium, fluids, and protein. Some people also need to limit potassium and phosphorus.
- Make exercise a routine part of your life.
Work with your doctor to design an exercise program that is right for you. Exercise may lower your risk for diabetes and high blood pressure.
- Don't smoke or use other tobacco products.
Smoking can lead to
atherosclerosisatherosclerosis , which reduces blood flow to the kidneys. - Limit your use of alcohol and avoid illegal drugs.
- Avoid taking medicines that can harm your kidneys.
These medicines include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Examples of these are ibuprofen and celecoxib. Let your doctor know all of the prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. And talk to your doctor before you take anything new.
- Avoid
dehydrationdehydration .Promptly treat illnesses, such as diarrhea, vomiting, or fever, that can cause dehydration. Be especially careful when you exercise or during hot weather.
- Avoid products containing magnesium.
These include antacids like Mylanta or Milk of Magnesia or laxatives like Citroma. These products increase your risk of having abnormally high levels of magnesium (hypermagnesemia), which may cause vomiting, diarrhea, or both.
- Avoid X-ray tests that require I.V.
dye (contrast material)dye (contrast material) .These include tests such as an angiogram, an
intravenous pyelogram (IVP)intravenous pyelogram (IVP) , and some CT scans. I.V. dye can cause more kidney damage. - Make sure that your doctor knows about any tests that you are scheduled to have, like an MRI.
Learn more
-
Diabetes: Checking Your Blood SugarDiabetes: Checking Your Blood Sugar -
Fitness: Getting and Staying ActiveFitness: Getting and Staying Active -
High Blood Pressure: Checking Your Blood Pressure at HomeHigh Blood Pressure: Checking Your Blood Pressure at Home -
Kidney Disease: Changing Your DietKidney Disease: Changing Your Diet -
Chronic Kidney Disease: Medicines to Be Careful WithChronic Kidney Disease: Medicines to Be Careful With -
Quitting SmokingQuitting Smoking -
Weight ManagementWeight Management
Medicines
Although medicine cannot reverse chronic kidney disease, it's often used to help treat symptoms and problems caused by kidney disease. Medicines are also used to slow further kidney damage.
Medicines can be used to treat problems such as:
- Anemia. Erythropoiesis-stimulating (ESA) therapy and iron replacement therapy can be used.
- A buildup of fluid. Diuretics are used for this.
- High blood pressure. ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), beta-blockers, or calcium channel blockers may be used.
- Electrolyte imbalances.
- Protein in your urine or heart failure. Medicines used may include ACE inhibitors and ARBs.
Medicines, like ESA therapy and iron, may be used during dialysis to treat anemia. Anemia often develops in advanced chronic kidney disease. Your doctor might also suggest taking vitamin D to help keep your bones strong.
If you have a kidney transplant, you'll have to take medicines called immunosuppressants. They help prevent your body from
Learn more
-
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) InhibitorsAngiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors -
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs)Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
Surgery
If you have chronic kidney disease that gets worse, you may be able to have a kidney transplant. You might be considered a good candidate if you don't have significant heart, lung, or liver disease or other diseases, such as cancer, which might decrease your life span.
Most experts agree that it's the best option for people with kidney failure. In general, people who have kidney transplants live longer than people treated with dialysis.
You may have to wait for a kidney to be donated. If so, you will need to have dialysis while you wait. Also, it may be hard to find a good match for your blood and tissue types. Sometimes, even when the match is good, the body rejects the new kidney.
After a kidney transplant, you will have to take medicines called immunosuppressants. These medicines help prevent your body from
Learn more
-
Kidney TransplantKidney Transplant
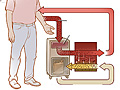
Dialysis
Dialysis is a mechanical process that performs the work that healthy kidneys would do. It clears wastes and extra fluid from the body. And it restores the proper balance of chemicals (
The two types of dialysis used to treat severe chronic kidney disease are:
-
HemodialysisHemodialysis . -
This uses a man-made membrane called a dialyzer to clean your blood. You are connected to the dialyzer by tubes attached to two blood vessels. Before treatments can begin, a surgeon creates a site where blood can flow in and out of your body. This is called the
dialysis accessdialysis access . -
Peritoneal dialysisPeritoneal dialysis . -
This uses the lining of your belly (
peritoneal membraneperitoneal membrane ) to clean your blood. Before you can begin, a surgeon needs to place a catheter in your belly to create the dialysis access.
Learn more
-
Advance Care Planning: Should I Stop Kidney Dialysis?Advance Care Planning: Should I Stop Kidney Dialysis? -
HemodialysisHemodialysis -
Kidney Failure: Should I Start Dialysis?Kidney Failure: Should I Start Dialysis? -
Kidney Failure: What Type of Dialysis Should I Have?Kidney Failure: What Type of Dialysis Should I Have? -
Kidney Failure: When Should I Start Dialysis?Kidney Failure: When Should I Start Dialysis? -
Peritoneal DialysisPeritoneal Dialysis
Current as of: October 11, 2024
Author:
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.
Related Links
Page Footer
I want to...
Audiences
Secure Member Sites
The Cigna Group Information
Disclaimer
Individual and family medical and dental insurance plans are insured by Cigna Health and Life Insurance Company (CHLIC), Cigna HealthCare of Arizona, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Illinois, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Georgia, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of North Carolina, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of South Carolina, Inc., and Cigna HealthCare of Texas, Inc. Group health insurance and health benefit plans are insured or administered by CHLIC, Connecticut General Life Insurance Company (CGLIC), or their affiliates (see
All insurance policies and group benefit plans contain exclusions and limitations. For availability, costs and complete details of coverage, contact a licensed agent or Cigna sales representative. This website is not intended for residents of New Mexico.