Skip to main navigation
Skip to main content
Skip to footer
For
Medicare
For
Providers
For
Brokers
For
Employers
Español
For Individuals & Families:
For Individuals & Families
Medical
Dental
Other Supplemental
Explore coverage through work
How to Buy Health Insurance
Types of Dental Insurance
Open Enrollment vs. Special Enrollment
See all topics
Shop for Medicare plans
Member Guide
Find a Doctor
Log in to myCigna
Home
Knowledge Center
Wellness Library
Dental Fillings (Restorations)
Dental Fillings (Restorations)
Treatment Overview
A filling is a material that your dentist uses to fill a cavity after the dentist removes any tooth decay. To fill a tooth, your dentist will numb the area, drill out the decay, and put in a filling. There are many types of fillings.
Types of fillings
Fillings can be made from many types of material. Talk to your dentist about which type would be best for you.
- Amalgam is the easiest material for a dentist to use. It's the fastest and least costly choice. Amalgam is a mixture of mercury, silver, and tin or other metals.
- Composite resins are tooth-colored fillings. Composite resin is easier than gold for a dentist to work with. And it usually costs less than gold.
- Ionomers are tooth-colored materials that dentists often use for small cavities or cavities between teeth. Some ionomers release small amounts of fluoride. This may help you if you often get cavities.
- Gold is costly and is harder for your dentist to work with. This makes the procedure take longer and cost more.
- Ceramics are costly tooth-colored fillings. They require special equipment and may require dental lab support. You may need several appointments.
What To Expect
What To Expect
After your dentist has filled the cavity, your lips and gums may stay numb for a few hours until the numbing medicine wears off. To avoid injuring your mouth, be careful not to chew on your numb lip or cheek.
Your filled tooth may be sensitive to heat and cold for days to weeks after you get the filling. Talk to your dentist about toothpastes that may help you with this discomfort. Tell your dentist if your teeth are too sensitive after you get a filling. This problem can usually be treated.
Why It Is Done
Why It Is Done
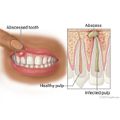
You need a filling when tooth decay has caused a hole (cavity) to form on a tooth surface. If you don't get a filling, the cavity will get worse. It may cause pain and then an abscess. This may lead to more severe problems, such as bone loss.
How Well It Works
How Well It Works
A filling repairs the tooth and stops tooth decay. Over a long period of time, you may need to replace a worn-out filling.
Risks
Risks
There is almost no risk involved in having a cavity filled.
If you have certain heart problems, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics before a dental procedure. Some procedures can cause bacteria in the mouth to enter the bloodstream and cause infections in other parts of the body. The antibiotics lower your risk of getting an infection in your heart called endocarditis.
Current as of: August 6, 2023
Author: Healthwise Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Healthwise, visit Healthwise.org.
© 1995-2024 Healthwise, Incorporated. Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Healthwise, Incorporated.
<cipublic-spinner variant="large"><span>Loading…</span></cipublic-spinner>