Treatment Option Overview
There are different types of treatment for patients with myelodysplastic syndromes.
Different types of treatment are available for patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Some treatments are standard (the currently used treatment), and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
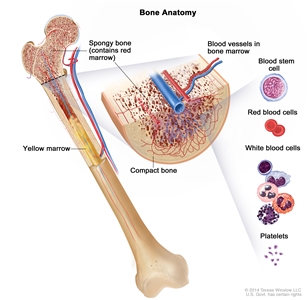
Treatment for myelodysplastic syndromes includes supportive care, drug therapy, and stem cell transplantation.
Patients with a myelodysplastic syndrome who have symptoms caused by low blood counts are given supportive care to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. Drug therapy may be used to slow progression of the disease. Certain patients can be cured with aggressive treatment with chemotherapy followed by stem cell transplant using stem cells from a donor.
The following types of treatment are used:
Supportive care
Supportive care is given to lessen the problems caused by the disease or its treatment. Supportive care may include the following:
- Transfusion therapy
Transfusion therapy (blood transfusion) is a method of giving red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets to replace blood cells destroyed by disease or treatment. A red blood cell transfusion is given when the red blood cell count is low and signs or symptoms of anemia, such as shortness of breath or feeling very tired, occur. A platelet transfusion is usually given when the patient is bleeding, is having a procedure that may cause bleeding, or when the platelet count is very low.
Patients who receive many blood cell transfusions may have tissue and organ damage caused by the buildup of extra iron. These patients may be treated with iron chelation therapy to remove the extra iron from the blood.
- Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents
Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) may be given to increase the number of mature red blood cells made by the body and to lessen the effects of anemia. Sometimes granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) is given with ESAs to help the treatment work better.
- Antibiotic therapy
Antibiotics may be given to fight infection.
Drug therapy
- Lenalidomide
Patients with myelodysplastic syndrome associated with an isolated del(5q) chromosome abnormality who need frequent red blood cell transfusions may be treated with lenalidomide. Lenalidomide is used to lessen the need for red blood cell transfusions.
- Immunosuppressive therapy
Antithymocyte globulin (ATG) works to suppress or weaken the immune system. It is used to lessen the need for red blood cell transfusions.
- Azacitidine and decitabine
Azacitidine and decitabine are used to treat myelodysplastic syndromes by killing cells that are dividing rapidly. They also help genes that are involved in cell growth to work the way they should. Treatment with azacitidine and decitabine may slow the progression of myelodysplastic syndromes to acute myeloid leukemia.
- Chemotherapy used in acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
Patients with a myelodysplastic syndrome and a high number of blasts in their bone marrow have a high risk of acute leukemia. They may be treated with the same chemotherapy regimen used in patients with acute myeloid leukemia.
Chemotherapy with stem cell transplant
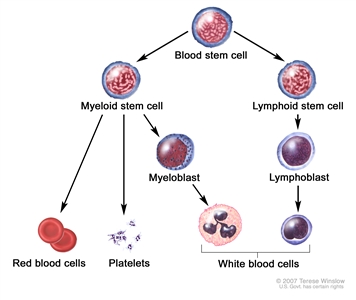
Chemotherapy is given to kill cancer cells. Healthy cells, including blood -forming cells, are also destroyed by the cancer treatment. Stem cell transplant is a treatment to replace the blood-forming cells. Stem cells (immature blood cells) are removed from the blood or bone marrow of the patient or a donor and are frozen and stored. After the patient completes chemotherapy, the stored stem cells are thawed and given back to the patient through an infusion. These reinfused stem cells grow into (and restore) the body's blood cells.
This treatment may not work as well in patients whose myelodysplastic syndrome was caused by past treatment for cancer. 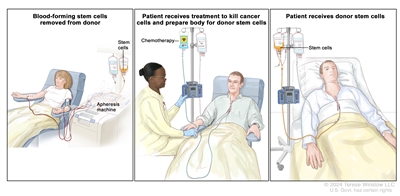
Donor stem cell transplant. (Step 1): Four to five days before donor stem cell collection, the donor receives a medicine to increase the number of stem cells circulating through their bloodstream (not shown). The blood-forming stem cells are then collected from the donor through a large vein in their arm. The blood flows through an apheresis machine that removes the stem cells. The rest of the blood is returned to the donor through a vein in their other arm. (Step 2): The patient receives chemotherapy to kill cancer cells and prepare their body for the donor stem cells. The patient may also receive radiation therapy (not shown). (Step 3): The patient receives an infusion of the donor stem cells.
New types of treatment are being tested in clinical trials.
Information about clinical trials is available from the NCI website.
Treatment for myelodysplastic syndromes may cause side effects.
For information about side effects caused by treatment for cancer, visit our Side Effects page.
Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial.
For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
Many of today's standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment.
Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward.
Patients can enter clinical trials before, during, or after starting their treatment.
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring (coming back) or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCI's clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Follow-up tests may be needed.
As you go through treatment, you will have follow-up tests or check-ups. Some tests that were done to diagnose or stage the cancer may be repeated to see how well the treatment is working. Decisions about whether to continue, change, or stop treatment may be based on the results of these tests.
Some of the tests will continue to be done from time to time after treatment has ended. The results of these tests can show if your condition has changed or if the cancer has recurred (come back).